
Trace
- ARM Instruction Set Format 2010.07.28
- java 연습문제 2010.07.27
- [100726]JAVA 기본 자료 타입, 기본 입출력, 연산자 2010.07.27
- 안드로이드 개발환경 구축 2010.07.25
- u-boot 분석 - 디렉토리 구조 2010.07.22
- U-Boot의 Makefile 분석 2010.07.22
- u-boot 1.16 소스 2010.07.22
- U-Boot 분석(5) 2010.07.22
- U-Boot 분석(4) 2010.07.22
- U-Boot 분석(3) 2010.07.22
ARM Instruction Set Format

java 연습문제
import java.util.*;
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int com, eng, math, java;
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("점수 : ");
com = input.nextInt();
eng = input.nextInt();
math = input.nextInt();
java = input.nextInt();
int sum = com + eng + math + java;
double avg = (double)sum / 4;
System.out.println("총점 : " + sum);
System.out.println("평균 : " + avg);
}
}

2.
import java.util.*;
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수값 : ");
int num = input.nextInt();
System.out.println("제곱 : " + (num * num));
System.out.println("세제곱 : " + (num * num * num));
}
} 
3.
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int pay = 10000;
int price = 3500;
int extra = (int)(price * 0.1);
int cnt = 2;
int total = (price + extra) * 2;
System.out.println("지불한 돈 : " + pay);
System.out.println("까페 모카 단가 : " + price);
System.out.println("수량 : " + cnt);
System.out.println("부가세 : " + extra);
System.out.println("상품 총액 : " + total);
System.out.println("거스름돈 : " + (pay - total));
}
}

4.
import java.util.*;
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수값 : ");
int num = input.nextInt();
System.out.println("천의 자리 : " + (num / 1000));
num %= 1000;
System.out.println("백의 자리 : " + (num / 100));
num %= 100;
System.out.println("십의 자리 : " + (num / 10));
num %= 10;
System.out.println("일의 자리 : " + num);
}
} 
5.
import java.util.*;
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("시간(초) : ");
int sec = input.nextInt();
int total = sec;
int hour = sec / 3600;
sec %= 3600;
int min = sec / 60;
sec %= 60;
System.out.println(total + "초는 " + hour + "시간 " + min + "분 " + sec + "초이다.");
}
}

6.
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("\'A\'+1\t\'A\'+2\t\'A\'+3");
System.out.println("---------------------------------------");
System.out.println((char)('A'+1) + "\t" + (char)('A'+2) + "\t" + (char)('A'+3));
}
} 
7.
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
double r = 5.0;
double v = 3.14 * r * r;
System.out.println("반지름 : " + r);
System.out.println("부피 : " + v);
}
} 
8.
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
double cm = 162.56;
double inch = cm / 2.54;
double pit = inch / 12;
inch %= 12;
System.out.println(cm + "cm는 " + (int)pit + "피트 " + (int)inch + "인치이다.");
}
} 
9.
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
double pit = 5;
double inch = 4;
double tinch = pit * 12 + 4;
double cm = tinch * 2.54;
System.out.println((int)pit + "피트 " + (int)inch + "인치는 "+ cm +"cm");
}
} 
[100726]JAVA 기본 자료 타입, 기본 입출력, 연산자
식별자
: 프로그램을 작성하다 보면 클래스나 메소드 변수 등에 직접 이름을 주어야 하는 경우가 생긴다. 이러한 클래스 이름, 메소드 이름, 변수 등과 같은 이름을 식별자라고 한다.
<< 식별자 명명 규칙
- 영문자(A~Z, a~z)와 숫자(0~9)와 '_', '$'의 조합으로 만들어진다.
- 첫 글자는 반드시 영문자나 '_'로 시작하여야 한다. 숫자로 시작해서는 안 된다.
- 식별자는 철자가 같다고 해도 대소문자를 구분하기 때문에 조심해야 한다.
- 자바에서 사용되는 예약어는 식별자로 사용할 수 없다.
- 식별자는 가급적이면 자기 역할에 맞는 이름을 부여한다.
자바 자료 타입
|
값 |
자료 타입 |
디폴트 값 |
크기 |
|
정수 |
byte |
0 |
8 bit |
|
short |
0 |
16 bit |
|
|
Int |
0 |
32 bit |
|
|
long |
0 |
64 bit |
|
|
실수 |
float |
0.0 |
32 bit |
|
double |
0.00 |
64 bit |
|
|
true/false |
boolean |
False |
1 bit |
|
유니코드 |
char |
U0000 |
16 bit |
문자형
자바에서 char형은 문자를 표현하기 위해 16비트 유니코드(Unicode) 문자 체계를 사용한다.
기본 입출력
자바의 기본 출력
출력을 위한 메소드는 println(), print(), printf()와 같이 3가지 형태로 제공된다.
간단한 출력 예제
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("println()");
System.out.print("print()");
System.out.printf("%s\n", "printf()");
}
} 
자바의 기본 입력
자바에서는 표준 입력 장치인 키보드에 대해서 System 클래스에 in라는 객체를 마련해 두었다. System.in 객체로 read() 메소드를 호출하여 키보드에서 데이터를 입력 받을 수 있다.
public abstract int read() throws 간단한 입력 예제 - 키보드에서 문자 한개 입력받기
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int data = 0;
System.out.print("Input Character : ");
data = System.in.read();
System.out.println(data);
System.out.println((char)data);
}
} 
간단한 입력 예제 - Scanner 클래스를 사용하여 키보드에서 정수 입력받기
import java.util.*;
public class Exam {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int a, b, c;
System.out.print("정수 데이터 2개 입력 >> ");
a = input.nextInt();
b = input.nextInt();
c = a + b;
System.out.printf("%3d + %3d = %4d", a, b, c);
}
} 
연산자
산술 연산자
|
구분 |
연산자 |
의미 |
|
단항 산술 연산자 |
+ |
양 수 |
|
- |
음 수 |
|
|
이항 산술 연산자 |
+ |
덧 셈 |
|
- |
뺄 셈 |
|
|
* |
곱 셈 |
|
|
/ |
나눗셈 |
|
|
% |
나머지 |
|
연산자 |
형 태 |
연산자 호칭 |
설명 |
|
++ |
++x |
전위 증가 연산자 |
연산 전에 x값 증가 |
|
x++ |
후위 증가 연산자 |
연산 후에 x값 증가 |
|
|
-- |
--x |
전위 감소 연산자 |
연산 전에 x값 감소 |
|
x-- |
후위 감소 연산자 |
연산 후에 x값 감소 |
관계 연산자
|
> |
op1 > op2 |
op1이 op2보다 크다 |
|
>= |
op1 >= op2 |
op1이 op2보다 크거나 같다 |
|
< |
op1 < op2 |
op1이 op2보다 작다 |
|
<= |
op1 <= op2 |
op1이 op2보다 작거나 같다 |
|
== |
op1 == op2 |
op1와 op2가 같다 |
|
!= |
op1 != op2 |
op1와 op2가 같지 않다 |
|
Instanceof |
op1 instanceof op2 |
op1이 op2의 인스턴스이다 |
논리 연산자
|
&& |
op1 && op2 |
op1과 op2가 모드 true이면 true, 그렇지 않으면 false |
|
|| |
op1 || op2 |
op1과 op2 둘 중 하나 이상이 true이면 true, 모두 false 이면 false |
|
! |
!op |
op가 true이면 false, false이면 true |
비트 연산자
|
& |
op1 & op2 |
op1과 op2 각 비트 단위의 논리곱 |
|
| |
op1 | op2 |
op1과 op2 각 비트 단위의 논리합 |
|
^ |
op1 ^ op2 |
op1과 op2 각 비트 단위의 배타적 논리곱 |
|
~ |
~op |
비트 단위의 1의 보수 |
|
>> |
op1 >> op2 |
op1과 op2만큼 오른쪽으로 이동 |
|
<< |
op1 << op2 |
op1과 op2만큼 왼쪽으로 이동 |
|
>>> |
op1 >>> op2 |
op1과 op2만큼 오른쪽으로 이동 왼쪽에는 항상 부호에 상관없이 0이 채워진다 |
안드로이드 개발환경 구축
: http://java.sun.com 에서 Java SE 버젼을 설치 한다.
2. eclipse 설치
: Eclipse IDE for Java EE Developers 이나 Eclipse Classic 버젼을 설치한다.(http://www.eclipse.org)
3. Android ADT 설치(Android Eclipse 플러그인)
: 설치된 eclipse를 실행한다. [Help - Install New Software...]를 클릭한다.

다음과 같은 창이 뜰 것이다. 오른쪽 상단에 Add 버튼을 누르고 다음과 같이 입력한다.

https://dl-ssl.google.com/android/eclipse/

Developer Tools라는 항목이 생겼을 것이다. Developer Tools 항목을 클릭해 전체 선택하고 Next 버튼을 누르면 Eclipse가 이 소프트웨어를 다운받고 설치까지 자동으로 수행한다.
4. Android SDK 설치
: http://developer.android.com 에서 Android SDK를 다운받는다. 다운 받은 SDK를 압축을 푼 후 적당한 디렉토리에 설치한다.(SDK 버전 2.0부터는 배포 용량이 너무 커져서 배포 파일에는 꼭 필요한 것들만 포함되어 있으며 더 필요한 부분은 온라인으로 다운받도록 변경되었다.)
ADT에게 SDK가 어디 있는지 위치를 설정한다. Eclipse [Window-Preference]를 클릭하고, 왼쪽 메뉴에서 Android를 선택한 후 SDK 폴더의 위치를 지정한다.

(현재 상태는 기본 SDK외에 추가로 SDK가 더 설치된 상태다. 문서 쓰는 시점이 다 설치한 후라...)
SDK의 위치를 지정했다면 다음은 추가로 더 필요한 SDK 요소들을 설치한다. [Window-Android SDK and AVR Manager]을 클릭한다. 왼쪽 메뉴에 Available Packages를 선택하면 설치 가능한 목록들이 나열되는데 필요한 버전을 설치하면 된다.

필요한 SDK를 선택한 후 [Install Selected]를 눌러 설치를 시작한다.
5. AVD(Android Virtual Device) 생성
: 안드로이드 어플를 직접 돌려 볼 수 있는 안드로이드폰 에뮬레이터를 생성한다. Eclipse [Window-Android SDK and AVD Manager]를 클릭한 후 왼쪽 메뉴 Virtual Device 페이지를 선택한다. 새로운 AVD를 생성하기 위해 New 버튼을 누른 후 다음과 같이 입력한다.

AVD 생성 후 Start 버튼을 누르면 에뮬레이터가 실행 된다... 다음은 에뮬레이트가 실행된 화면이다.

u-boot 분석 - 디렉토리 구조
./doc/
- 여러개가 있다.
./tools/
아직 미지(?)의 디렉토리도 있고, 정확히 이해하지 못하는 디렉토리나 잘못 할고 있는 디렉토리도 있다. 따라서 이 글은 수정을 통해서 업데이트 해야겠다.
출처 : http://inusing.tistory.com/17
U-Boot의 Makefile 분석
이 항목은 U-Boot를 어떤 CPU로 사용하는 Board용으로 빌드 할 것인지를 결정합니다.
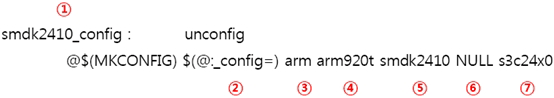
[1~7 항 목별 역할]
①U-Boot를 빌드 할 Configuration의 이름
U-Boot를 특정 보드를 위하여, 빌드 할 수 있도록 해주는 구분자입니다. 실제로 U-Boot 컴파일 시 “make smdk2410_config”라고 입력하면, U-Boot는 SMDK2410 보드용으로 컴파일 될 수 있도록 설정됩니다.
②“make smdk2410_config”를 입력하면,
위의 Makefile에서는 mkconfig라는 유틸리티를 호출하여 mkconfig에 ③~⑦ 번 항목을 인자로 입력합니다. mkconfig 스크립트는 이 인자를 입력 받아서 컴파일 환경 설정을 진행하게 됩니다.
$(@:_config=) 항목의 경우 위의 “smdk2410_config” 라는 항목이며, 여기서 “smdk2410”이라는 항목만을 인자로 받아서, mkconfig에 전달하게 됩니다.
“smdk2410”이라는 항목은 mkconfig에서 BOARD_NAME을 설정하는데 사용되며,
다음은 mkconfig에서 이 인자를 전달 받아서 Board Name을 설정하는 항목입니다.
while [ $# -gt 0 ]
; do
case
"$1" in
--)
shift ; break ;;
-a) shift ; APPEND=yes ;;
-n) shift ; BOARD_NAME="${1%%_config}" ;
shift ;;
*)
break ;;
esac
done
[ "${BOARD_NAME}"
] || BOARD_NAME="$1"
[ $# -lt 4 ] && exit 1
[ $# -gt 6 ]
&& exit 1
echo "Configuring for ${BOARD_NAME} board..."
위의 BOARD_NAME이라는 항목에는 “smdk2410_config”에서 “_config”를 제외한 “smdk2410”을 $1 인자로 받아 처리하는 mkconfig 스크립트의 루틴입니다. 이 루틴 때문에 U-Boot 컴파일 시 “make smdk2410_config”을 입력하면,"Configuring for smdk2410 board..."라는 메시지가 화면에 출력되게 됩니다.
③CPU의 아키텍처를 입력하는 부분으로 ARM, MIPS등 CPU 아키텍처들 별로 상이하게 사용되는 어셈블러 랭귀지를 구분하기 위해 만들어진 항목입니다. mkconfig에 두 번째 인자로 전달되며 [ARCH] 라는 항목으로 인식됩니다. 이 항목은 다음과 같은 디렉터리를 컴파일 하도록 설정합니다.- U-Boot의 “include/” 디렉터리 내의 헤더 파일들에 대한 컴파일 항목
ㆍ“include/asm-[ARCH]/” 를 “include/asm/” 이라는 이름으로 심볼릭 링크를 생성하고 이 항목들을 이 항목들을 소스 컴파일 시 include시킵니다..
ㆍ“include/asm-[ARCH]/proc- armv/”를 “proc-armv/”라는 이름으로 심볼릭 링크를 생성하고 이 항목들을 소스 컴파일 시에 include시킵니다. - U-Boot 소스의 루트 디렉터리에 대한 컴파일 항
ㆍ“lib_[ARCH]/” 디렉터리를 컴파일 합니다.
④CPU의 종류를 입력하는 부분으로 ARM 계열 CPU의 각 계열들을 구분하기 위해서 만들어진 항목입니다. 각 CPU 계열별로 특화된 항목에 대한 부분이 담겨있습니다. mkconfig에 세 번째 인자로 전달되며 [CPU] 라는 항목으로 인식됩니다. 이 항목은 다음과 같은 이름의 디렉터리를 컴파일 하도록 명령합니다.
- U-Boot 소스의 “cpu/” 디렉터리에 대한 컴파일 항목
“cpu/[CPU]/” 디렉터리를 컴파일 합니다.
⑤Board의 이름을 입력하는 항목으로 Board의 종류에 따라 특화된 항목에 대한 부분이 담겨있습니다. mkconfig에 네 번째 인자로 전달되며, [BOARD] 라 는 항목으로 인식됩니다. 이 항목은 다음과 같은 이름의 디렉터리를 컴파일 하도록 명령합니다.
- U-Boot 소스의 “/board” 디렉터리에 대한 컴파일 항목 “board/[BOARD]/” 디렉터리를 컴파일 합니다.
⑥Board를 제조한 Vendor에 대한 이름을 입력하는 항목으로 한 벤더에서 여러 가지의 Board를 출시했을 경우, 편리하게 분류 하기 위하여 만든 항목 입니다. 특정한 벤더가 없을 경우 “NULL”로 처리하면 자동으로 ⑤번 에서 설명한 항목만을 가지고 컴파일 합니다.
- U-Boot 소스의 “board/” 디렉터리에 대한 컴파일 항목
“board/[VENDOR]/[BOARD]/” 디렉터리를 컴파일 합니다.
⑦SoC(이하 System On Chip)의 모델명을 입력하는 항목으로, 각 CPU 아키텍처와 계열을 탑재한 각 CPU 벤더의 SoC에 담겨있는 특화된 기능을 지원하기 위해 만들어진 항목입니다. mkconfig에 여섯 번째 인자로 전달되며,[SoC] 라는 항목으로 인식됩니다. 이 항목은 다음과 같은 이름의 디렉터리를 컴파일 하도록 명령합니다.
- U-Boot 소스의 “cpu/” 디렉터리에 대한 컴파일 항목
“cpu/[CPU]/[SoC]/” 디렉터리를 컴파일 합니다.
- U-Boot의 “include/” 디렉터리 내의 헤더 파일들에 대한 컴파일 항목
“include/asm-[ARCH]/[SoC]/” 를 “asm/arch/”라는 이름으로 심볼릭 링크를 생성하고 이 항목들을 이 항목들을 소스 컴파일 시에 include 시킵니다.
출처 : http://blog.naver.com/hirou6/80107355464
u-boot 1.16 소스
U-Boot 분석(5)
Board.C
start.s에서 start_armboot()로 제어가 넘어왔다. 이 함수는 board.c에 정의되어있다.
board.c를 보도록 하자. board.c는 /lib_arm/에 위치해 있다.
/*
* (C) Copyright 2002
* Wolfgang Denk, DENX Software
Engineering, wd@denx.de.
*
* (C) Copyright 2002
*
Sysgo Real-Time Solutions, GmbH <www.elinos.com>
* Marius
Groeger <mgroeger@sysgo.de>
*
*
See file CREDITS for list of people who contributed to this
*
project.
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute
it and/or
* modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public
License as
* published by the Free Software Foundation; either
version 2 of
* the License, or (at your option) any later version.
*
*
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
*
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
*
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU
General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have
received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with this
program; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 59
Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston,
* MA 02111-1307 USA
*/
#include <common.h>
#include <command.h>
#include
<malloc.h>
#include <devices.h>
#include
<version.h>
#include <net.h>
#ifdef CONFIG_DRIVER_SMC91111
#include "../drivers/smc91111.h"
#endif
#ifdef
CONFIG_DRIVER_LAN91C96
#include "../drivers/lan91c96.h"
#endif
#if (CONFIG_COMMANDS & CFG_CMD_NAND)
void nand_init (void);
#endif
ulong monitor_flash_len;
#ifdef CONFIG_HAS_DATAFLASH
extern int AT91F_DataflashInit(void);
extern
void dataflash_print_info(void);
#endif
#ifndef CONFIG_IDENT_STRING
#define CONFIG_IDENT_STRING ""
#endif
const char version_string[] =
U_BOOT_VERSION" (" __DATE__ " - "
__TIME__ ")"CONFIG_IDENT_STRING;
#ifdef CONFIG_DRIVER_CS8900
extern void cs8900_get_enetaddr (uchar
* addr);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DRIVER_RTL8019
extern void rtl8019_get_enetaddr
(uchar * addr);
#endif
/*
* Begin and End of memory area for malloc(), and current "brk"
*/
static
ulong mem_malloc_start = 0;
static ulong mem_malloc_end = 0;
static
ulong mem_malloc_brk = 0;
static
void mem_malloc_init (ulong dest_addr)
{
mem_malloc_start
= dest_addr;
mem_malloc_end = dest_addr + CFG_MALLOC_LEN;
mem_malloc_brk
= mem_malloc_start;
memset ((void *) mem_malloc_start, 0,
mem_malloc_end -
mem_malloc_start);
}
void *sbrk (ptrdiff_t increment)
{
ulong old = mem_malloc_brk;
ulong
new = old + increment;
if ((new < mem_malloc_start) || (new > mem_malloc_end)) {
return
(NULL);
}
mem_malloc_brk = new;
return ((void *) old);
}
/************************************************************************
*
Init Utilities *
************************************************************************
*
Some of this code should be moved into the core functions,
* or
dropped completely,
* but let's get it working (again) first...
*/
/* console에 사용할 UART의 baud rate를 설정 */
static int init_baudrate
(void)
{
DECLARE_GLOBAL_DATA_PTR;
uchar tmp[64]; /* long enough for environment variables */
int i
= getenv_r ("baudrate", tmp, sizeof (tmp));
gd->bd->bi_baudrate
= gd->baudrate = (i > 0)
? (int) simple_strtoul (tmp, NULL,
10)
: CONFIG_BAUDRATE;
return (0);
}
/* 설정된 정보를 화면에 출력한다. */
/* uboot version및 code, data, stack의
위치를 console에 출력 */
static int display_banner (void)
{
printf
("\n\n%s\n\n", version_string);
printf ("U-Boot code: %08lX ->
%08lX BSS: -> %08lX\n",
_armboot_start, _bss_start, _bss_end);
#ifdef
CONFIG_MODEM_SUPPORT
puts ("Modem Support enabled\n");
#endif
#ifdef
CONFIG_USE_IRQ
printf ("IRQ Stack: %08lx\n", IRQ_STACK_START);
printf
("FIQ Stack: %08lx\n", FIQ_STACK_START);
#endif
return (0);
}
/*
* WARNING: this code looks "cleaner" than the PowerPC
version, but
* has the disadvantage that you either get nothing, or
everything.
* On PowerPC, you might see "DRAM: " before the system
hangs - which
* gives a simple yet clear indication which part of
the
* initialization if failing.
*/
/* DRAM셋팅후 화면에 출력 */
static
int display_dram_config (void)
{
DECLARE_GLOBAL_DATA_PTR;
int
i;
puts ("RAM Configuration:\n");
for(i=0; i<CONFIG_NR_DRAM_BANKS; i++) {
printf ("Bank #%d:
%08lx ", i, gd->bd->bi_dram[i].start);
print_size
(gd->bd->bi_dram[i].size, "\n");
}
return (0);
}
static void display_flash_config (ulong size)
{
puts ("Flash:
");
print_size (size, "\n");
}
/*
* Breathe some life into the board...
*
*
Initialize a serial port as console, and carry out some hardware
*
tests.
*
* The first part of initialization is running from
Flash memory;
* its main purpose is to initialize the RAM so that we
*
can relocate the monitor code to RAM.
*/
/*
* All attempts to come up with a "common" initialization
sequence
* that works for all boards and architectures failed: some
of the
* requirements are just _too_ different. To get rid of the
resulting
* mess of board dependent #ifdef'ed code we now make the
whole
* initialization sequence configurable to the user.
*
*
The requirements for any new initalization function is simple: it
*
receives a pointer to the "global data" structure as it's only
*
argument, and returns an integer return code, where 0 means
*
"continue" and != 0 means "fatal error, hang the system".
*/
typedef int (init_fnc_t) (void);
/* 포인터 변수는 값으로 주소를 갖는다. 각 주소에 가보면 함수가 존재할것이다.
*/
init_fnc_t *init_sequence[] = {
cpu_init, /* basic cpu
dependent setup */
board_init, /* basic board dependent setup */
interrupt_init, /*
set up exceptions */
env_init, /* initialize environment */
init_baudrate, /*
initialze UART baudrate settings */
serial_init, /* serial
communications setup */
console_init_f, /* stage 1 init of console
*/
display_banner, /* say that we are here */
dram_init, /*
configure available RAM banks */
display_dram_config, /* SDRAM start
address, size를 console에 출력 */
#if defined(CONFIG_VCMA9)
checkboard,
#endif
NULL,
};
/* board와 관련된 모든 자원을 초기화 */
void start_armboot (void)
{
/* Global_data.h에 명시 register volatile gd_t *gd
asm("r8") */
DECLARE_GLOBAL_DATA_PTR;
ulong size;
init_fnc_t **init_fnc_ptr; /*
2차원 함수 배열. init_fnc_t *형은 *init_fnc_ptr의 데이터를 갖는다. 이는 어떠한 함수를 가리킬 것이고 이
함수들은 바로 위에 정의되어 있다. */
char *s;
/*
LCD controller설정 */
#if defined(CONFIG_VFD) ||
defined(CONFIG_LCD)
unsigned long addr;
#endif
/* 포인터 설정 */
/* Pointer is writable
since we allocated a register for it */
gd = (gd_t*)(_armboot_start
- CFG_MALLOC_LEN - sizeof(gd_t));
/* compiler optimization barrier
needed for GCC >= 3.4 */
__asm__ __volatile__("": : :"memory");
/* 메모리 클리어. 이 함수가 정의된 부분으로 가보면 gd부터 sizeof로
구한 영역만큼 0의 값을 넣어주는 함수이다. */
memset ((void*)gd, 0, sizeof
(gd_t));
gd->bd = (bd_t*)((char*)gd - sizeof(bd_t));
/* global_data struct의 data를 0으로 초기화 한다.
*/
/* gd->bd가리키는 영역을 gd_t크기만큼 0으로 만든다. */
memset
(gd->bd, 0, sizeof (bd_t));
/* 모니터코드의 flash에서의 길이를 구한다. */
monitor_flash_len
= _bss_start - _armboot_start;
/* board에 관련된 모든 자원을 초기화 한다. 바로 위의 함수배열로 정의되어
있다. 각각의 함수를 찾아보면서 어떤 동작을 하는지 알아보시길... */
/* cpu, board, interrupt,
env, baudrate, serial, console, display, dram등등.. */
for
(init_fnc_ptr = init_sequence;
*init_fnc_ptr; ++init_fnc_ptr) {
if ((*init_fnc_ptr)() != 0) {
/* error가 발생햇으니 reset하라고 출력하는 함수이다. */
hang
();
}
}
/* configure available FLASH banks */
size
= flash_init (); /* flash를 초기화 하고 size를 얻는다. */
display_flash_config
(size); /* flash의 size를 console에 출력한다. */
#ifdef CONFIG_VFD
# ifndef PAGE_SIZE
# define PAGE_SIZE 4096
# endif
/*
* reserve memory for VFD display (always full pages)
*/
/*
bss_end is defined in the board-specific linker script */
addr =
(_bss_end + (PAGE_SIZE - 1)) & ~(PAGE_SIZE - 1);
size =
vfd_setmem (addr);
gd->fb_base = addr;
#endif /* CONFIG_VFD */
#ifdef CONFIG_LCD
# ifndef PAGE_SIZE
# define PAGE_SIZE 4096
# endif
/*
* reserve memory for LCD display (always full pages)
*/
/*
bss_end is defined in the board-specific linker script */
addr =
(_bss_end + (PAGE_SIZE - 1)) & ~(PAGE_SIZE - 1);
size =
lcd_setmem (addr);
gd->fb_base = addr;
#endif /* CONFIG_LCD */
/* armboot_start is defined in the
board-specific linker script */
mem_malloc_init
(_armboot_start - CFG_MALLOC_LEN);
#if (CONFIG_COMMANDS & CFG_CMD_NAND)
puts ("NAND:");
nand_init(); /*
go init the NAND */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_HAS_DATAFLASH
AT91F_DataflashInit();
dataflash_print_info();
#endif
/* initialize environment */
env_relocate
(); /* flash에서 SDRAM으로 COPY한다. */
#ifdef CONFIG_VFD
/* must do this after the framebuffer is
allocated */
drv_vfd_init();
#endif /* CONFIG_VFD */
/* IP Address */
gd->bd->bi_ip_addr
= getenv_IPaddr ("ipaddr");
/* MAC Address */
{
int i;
ulong
reg;
char *s, *e;
uchar tmp[64];
i = getenv_r ("ethaddr", tmp, sizeof (tmp));
s = (i > 0) ?
tmp : NULL;
for (reg = 0; reg < 6; ++reg) {
gd->bd->bi_enetaddr[reg]
= s ? simple_strtoul (s, &e, 16) : 0;
if (s)
s = (*e) ?
e + 1 : e;
}
}
/* 설정되어 잇는 device가
있으면 초기화 한다.(i2c, LCD, keyboard) */
devices_init (); /* get
the devices list going. */
jumptable_init ();
console_init_r (); /* fully init console as a device */
#if defined(CONFIG_MISC_INIT_R)
/* miscellaneous platform
dependent initialisations */
misc_init_r ();
#endif
/* enable exceptions */
/* interrupt를
enable한다. */
enable_interrupts ();
/* Perform network card initialisation if
necessary */
#ifdef CONFIG_DRIVER_CS8900
cs8900_get_enetaddr
(gd->bd->bi_enetaddr);
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_DRIVER_SMC91111) || defined
(CONFIG_DRIVER_LAN91C96)
if (getenv ("ethaddr")) {
smc_set_mac_addr(gd->bd->bi_enetaddr);
}
#endif
/* CONFIG_DRIVER_SMC91111 || CONFIG_DRIVER_LAN91C96 */
/* Initialize from environment */
if
((s = getenv ("loadaddr")) != NULL) {
load_addr = simple_strtoul
(s, NULL, 16);
}
#if (CONFIG_COMMANDS & CFG_CMD_NET)
if
((s = getenv ("bootfile")) != NULL) {
copy_filename (BootFile, s,
sizeof (BootFile));
}
#endif /* CFG_CMD_NET */
#ifdef BOARD_LATE_INIT
board_late_init ();
#endif
/* main_loop() can return to retry autoboot,
if so just run it again. */
for (;;) {
main_loop (); /*
(TOPDIR)/common/main.c 여기서 main()함수로 제어가 넘어가게된다. */
}
/* NOTREACHED - no way out of command loop except booting */
}
void hang (void)
{
puts ("### ERROR ### Please RESET the
board ###\n");
for (;;);
}
#ifdef CONFIG_MODEM_SUPPORT
/* called from main loop
(common/main.c) */
extern void dbg(const char *fmt, ...);
int
mdm_init (void)
{
char env_str[16];
char *init_str;
int
i;
extern char console_buffer[];
static inline void
mdm_readline(char *buf, int bufsiz);
extern void enable_putc(void);
extern
int hwflow_onoff(int);
enable_putc(); /* enable serial_putc() */
#ifdef CONFIG_HWFLOW
init_str = getenv("mdm_flow_control");
if
(init_str && (strcmp(init_str, "rts/cts") == 0))
hwflow_onoff
(1);
else
hwflow_onoff(-1);
#endif
for (i = 1;;i++) {
sprintf(env_str, "mdm_init%d", i);
if
((init_str = getenv(env_str)) != NULL) {
serial_puts(init_str);
serial_puts("\n");
for(;;)
{
mdm_readline(console_buffer, CFG_CBSIZE);
dbg("ini%d:
[%s]", i, console_buffer);
if ((strcmp(console_buffer, "OK") == 0) ||
(strcmp(console_buffer,
"ERROR") == 0)) {
dbg("ini%d: cmd done", i);
break;
}
else /* in case we are originating call ... */
if
(strncmp(console_buffer, "CONNECT", 7) == 0) {
dbg("ini%d:
connect", i);
return 0;
}
}
} else
break;
/* no init string - stop modem init */
udelay(100000);
}
udelay(100000);
/* final stage - wait for connect */
for(;i > 1;) { /* if 'i'
> 1 - wait for connection
message from modem */
mdm_readline(console_buffer,
CFG_CBSIZE);
dbg("ini_f: [%s]", console_buffer);
if
(strncmp(console_buffer, "CONNECT", 7) == 0) {
dbg("ini_f:
connected");
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
/* 'inline' - We have to do it fast */
static inline void
mdm_readline(char *buf, int bufsiz)
{
char c;
char *p;
int
n;
n = 0;
p = buf;
for(;;) {
c = serial_getc();
/* dbg("(%c)", c); */
switch(c) {
case '\r':
break;
case '\n':
*p =
'\0';
return;
default:
if(n++ > bufsiz) {
*p = '\0';
return;
/* sanity check */
}
*p = c;
p++;
break;
}
}
}
#endif /*
CONFIG_MODEM_SUPPORT */
이로써 U-Boot분석에 필요한 파일들을 살펴보았다. 이후 각자가 사용하게 될 보드에 맞게 포팅을 할때 지금 까지 봐왔던 큰 흐름을 기억하고 그에 따르는 줄기들을 잘 분석했다면 어떤 파일들을 수정해야 하는지 감이 올 것이다. 아울러 데이터시트를 참조하는것은 기본이라는 걸 기억하면서 u-boot에 대한 공부는 마무리하도록 하겠다.(머지않아 다시 골머리를 썩겠지만 ㅋ)
6주 속성으로 배우기 무지 힘들다ㅠ.ㅠㅋ 시간 날때마다 추가적으로 분석하고 주석을 달아봐야겠다.
---------------
출처 : http://blog.naver.com/idrukawa/100054114578
U-Boot 분석(4)
memsetup.S
이전 start.S소스 중에서 cpu_init_crit()에서 memsetup으로 제어가 넘어왔다.
memsetup을 살펴보도록 하겠다.
/*
* A EEEE SSSS OOO PPPP
* A A E
S O O P P
* AAAAA EEEE SSSS O O PPPP
* A
A E S O O P
* A A EEEE SSSS OOO P
*
*
An Entertainment Solution On a Platform (AESOP) is a completely Open
Source
* based graphical user environment and suite of
applications for PDAs and other
* devices running Linux. It is
included in various embedded Linux distributions
* such as
OpenZaurus - http://www.aesop-embedded.org
*
*
*
This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
*
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
*
the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
*
(at your option) any later version.
*
* This program is
distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY
WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public
License for more details.
*
*
* Title : memsetup.S
* Author
:
* Created date : 2005. 06. 26. 23:05:30 KST
* Description
:
*
* $Revision: 1.1.1.1 $
* $Log: memsetup.S,v $
* Revision
1.1.1.1 2005/06/27 17:04:30 linuxpark
* Initial import.
*
*
*
*/
#ident "@(*) $Header:
/cvsroot/aesop-embedded/u-boot-aesop/board/aesop2440/memsetup.S,v
1.1.1.1 2005/06/27 17:04:30 linuxpark Exp $"
/*
* Memory Setup stuff - taken from blob memsetup.S
*
*
Copyright (C) 1999 2000 2001 Erik Mouw (J.A.K.Mouw@its.tudelft.nl)
and
* Jan-Derk Bakker (J.D.Bakker@its.tudelft.nl)
*
*
Modified for the Samsung SMDK2410 by
* (C) Copyright 2002
*
David Mueller, ELSOFT AG, <d.mueller@elsoft.ch>
*
*
See file CREDITS for list of people who contributed to this
*
project.
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute
it and/or
* modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public
License as
* published by the Free Software Foundation; either
version 2 of
* the License, or (at your option) any later version.
*
*
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
*
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
*
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU
General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have
received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with this
program; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 59
Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston,
* MA 02111-1307 USA
*/
#include <config.h>
#include <version.h>
/* some parameters for the board */
/*
*
* Taken from
linux/arch/arm/boot/compressed/head-s3c2410.S
*
* Copyright (C)
2002 Samsung Electronics SW.LEE <hitchcar@sec.samsung.com>
*
*/
#define BWSCON 0x48000000
/* BWSCON */
#define DW8 (0x0)
#define DW16 (0x1)
#define
DW32 (0x2)
#define WAIT (0x1<<2)
#define UBLB
(0x1<<3)
#define B1_BWSCON (DW32)
#define B2_BWSCON (DW16)
#define
B3_BWSCON (DW16 + WAIT + UBLB)
#define B4_BWSCON (DW16)
#define
B5_BWSCON (DW16)
#define B6_BWSCON (DW32)
#define
B7_BWSCON (DW32)
/* BANK0CON */
#define B0_Tacs 0x0 /* 0clk */
#define
B0_Tcos 0x0 /* 0clk */
#define B0_Tacc 0x7 /* 14clk */
#define
B0_Tcoh 0x0 /* 0clk */
#define B0_Tah 0x0 /* 0clk */
#define
B0_Tacp 0x0
#define B0_PMC 0x0 /* normal */
/* BANK1CON */
#define B1_Tacs 0x0 /* 0clk */
#define
B1_Tcos 0x0 /* 0clk */
#define B1_Tacc 0x7 /* 14clk */
#define
B1_Tcoh 0x0 /* 0clk */
#define B1_Tah 0x0 /* 0clk */
#define
B1_Tacp 0x0
#define B1_PMC 0x0
#define B2_Tacs 0x0
#define B2_Tcos 0x0
#define B2_Tacc
0x7
#define B2_Tcoh 0x0
#define B2_Tah 0x0
#define
B2_Tacp 0x0
#define B2_PMC 0x0
#define B3_Tacs 0x0 /* 0clk */
#define B3_Tcos 0x3 /* 4clk
*/
#define B3_Tacc 0x7 /* 14clk */
#define B3_Tcoh 0x1 /*
1clk */
#define B3_Tah 0x0 /* 0clk */
#define B3_Tacp
0x3 /* 6clk */
#define B3_PMC 0x0 /* normal */
#define B4_Tacs 0x0 /* 0clk */
#define B4_Tcos 0x0 /* 0clk
*/
#define B4_Tacc 0x7 /* 14clk */
#define B4_Tcoh 0x0 /*
0clk */
#define B4_Tah 0x0 /* 0clk */
#define B4_Tacp 0x0
#define
B4_PMC 0x0 /* normal */
#define B5_Tacs 0x0 /* 0clk */
#define B5_Tcos 0x0 /* 0clk
*/
#define B5_Tacc 0x7 /* 14clk */
#define B5_Tcoh 0x0 /*
0clk */
#define B5_Tah 0x0 /* 0clk */
#define B5_Tacp 0x0
#define
B5_PMC 0x0 /* normal */
#define B6_MT 0x3 /* SDRAM */
#define B6_Trcd 0x1
#define
B6_SCAN 0x1 /* 9bit */
#define B7_MT 0x3 /* SDRAM */
#define B7_Trcd 0x1 /* 3clk */
#define
B7_SCAN 0x1 /* 9bit */
/* REFRESH parameter */
#define REFEN 0x1 /* Refresh enable */
#define
TREFMD 0x0 /* CBR(CAS before RAS)/Auto refresh */
#define Trp
0x0 /* 2clk */
#define Trc 0x3 /* 7clk */
#define Tchr
0x2 /* 3clk */
#define REFCNT 1113 /* period=15.6us, HCLK=60Mhz,
(2048+1-15.6*60) */
/**************************************/
_TEXT_BASE:
.word TEXT_BASE
/* S3C2440의 데이터시트를 보면서 코드를 따라 차근차근 그려가며 분석해보면
재미있게 이해할 수 있다. */
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
.globl
memsetup // Linker에게 symbol처리 할 수 있도록
export
memsetup: // SMRDATA는 아직 메모리가 초기화 되지 않았으므로
// flash에서 읽기 위하여 r0에 상대적인 위치를 저장한다.
ldr
r0, =SMRDATA // SMRDATA address를 r0레지스터로 이동.
ldr r1,
_TEXT_BASE // _TEXT_BASE에 잇는 data를 r1레지스터로 이동.
sub r0,
r0, r1 // r0에 상대주소값을 저장한다. r0 := r0 - r1
ldr r1,
=BWSCON /* Bus Width Status Controller의 주소를 r1에
저장 */
add r2, r0, #13*4 // 13개의
word레지스터를 r0레지스터와 더한 후 r2레지스터로 이동.
//
13번 loop를 돌리기 위해 compare할 레지스터 setting(즉, end Address)
0: // 이곳으로
분기해
염.............................................................................
ldr
r3, [r0], #4 // r0가 가리키는 address의 data를 r3레지스터로
이동 후 r0값을 4증가시킨다.
str r3, [r1], #4 //
r1이 가리키는 address에 r3 data를 저장 후 r1값을 4증가시킨다.
cmp r2,
r0 // r2, r0값을 비교하여 그 결과 값을 CPSR에 setting
bne
0b // Z flag가
clear(0)이면
분기해라............................................................
// set(1)이면 다음 명령어 수행.
/*
everything is fine now */
mov pc,
lr // memsetup함수를 호출한 start.S의
cpu_init_crit으로 복귀한다.
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
.ltorg
/*
the literal pools origin */
SMRDATA:
.word
(0+(B1_BWSCON<<4)+(B2_BWSCON<<8)+(B3_BWSCON<<12)+(B4_BWSCON<<16)+(B5_BWSCON<<20)+(B6_BWSCON<<24)+(B7_BWSCON<<28))
.word
((B0_Tacs<<13)+(B0_Tcos<<11)+(B0_Tacc<<8)+(B0_Tcoh<<6)+(B0_Tah<<4)+(B0_Tacp<<2)+(B0_PMC))
.word
((B1_Tacs<<13)+(B1_Tcos<<11)+(B1_Tacc<<8)+(B1_Tcoh<<6)+(B1_Tah<<4)+(B1_Tacp<<2)+(B1_PMC))
.word
((B2_Tacs<<13)+(B2_Tcos<<11)+(B2_Tacc<<8)+(B2_Tcoh<<6)+(B2_Tah<<4)+(B2_Tacp<<2)+(B2_PMC))
.word
((B3_Tacs<<13)+(B3_Tcos<<11)+(B3_Tacc<<8)+(B3_Tcoh<<6)+(B3_Tah<<4)+(B3_Tacp<<2)+(B3_PMC))
.word
((B4_Tacs<<13)+(B4_Tcos<<11)+(B4_Tacc<<8)+(B4_Tcoh<<6)+(B4_Tah<<4)+(B4_Tacp<<2)+(B4_PMC))
.word
((B5_Tacs<<13)+(B5_Tcos<<11)+(B5_Tacc<<8)+(B5_Tcoh<<6)+(B5_Tah<<4)+(B5_Tacp<<2)+(B5_PMC))
.word ((B6_MT<<15)+(B6_Trcd<<2)+(B6_SCAN))
.word
((B7_MT<<15)+(B7_Trcd<<2)+(B7_SCAN))
.word
((REFEN<<23)+(TREFMD<<22)+(Trp<<20)+(Trc<<18)+(Tchr<<16)+REFCNT)
.word 0x32
.word 0x30
.word 0x30
---------------
출처 : http://blog.naver.com/idrukawa/100054113511
U-Boot 분석(3)
u-boot.lds의 ENTRY부분에서 _start로 제어가 넘겨졌었다.
이 _start는 start.S에 선언되어 있다.
start.S를 보도록 하자.
/*
* A EEEE SSSS OOO PPPP
* A A E
S O O P P
* AAAAA EEEE SSSS O O PPPP
* A
A E S O O P
* A A EEEE SSSS OOO P
*
*
An Entertainment Solution On a Platform (AESOP) is a completely Open
Source
* based graphical user environment and suite of
applications for PDAs and other
* devices running Linux. It is
included in various embedded Linux distributions
* such as
OpenZaurus - http://www.aesop-embedded.org
*
*
*
This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
*
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
*
the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
*
(at your option) any later version.
*
* This program is
distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY
WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public
License for more details.
*
*
* Title : start.S
* Author
:
* Created date : 2005. 06. 26. 23:20:34 KST
* Description
:
*
* $Revision: 1.1.1.1 $
* $Log: start.S,v $
* Revision
1.1.1.1 2005/06/27 17:03:41 linuxpark
* Initial import.
*
*
*
*/
#ident "@(*) $Header:
/cvsroot/aesop-embedded/u-boot-aesop/cpu/arm920t/start.S,v 1.1.1.1
2005/06/27 17:03:41 linuxpark Exp $"
/*
* armboot - Startup Code for ARM920 CPU-core
*
*
Copyright (c) 2001 Marius Gr?er <mag@sysgo.de>
* Copyright (c)
2002 Alex Z?ke <azu@sysgo.de>
* Copyright (c)
2002 Gary Jennejohn <gj@denx.de>
* Copyright (c) 2005
Junyoung Song <jun0song@kornet.net>
*
*
See file CREDITS for list of people who contributed to this
*
project.
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute
it and/or
* modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public
License as
* published by the Free Software Foundation; either
version 2 of
* the License, or (at your option) any later version.
*
*
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
*
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
*
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU
General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have
received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with this
program; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 59
Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston,
* MA 02111-1307 USA
*/
#include <config.h>
#include <version.h>
/*
*************************************************************************
*
*
Jump vector table as in table 3.1 in [1]
*
*************************************************************************
*/
.globl _start
_start: b reset /* exception의 처음인 0x00000000번지이다. 이 명령에 의해 reset로
branch한다. reset는 좀 더 아래에 선언되어있다.*/
ldr pc,
_undefined_instruction /* exception vector 설정 */
ldr pc,
_software_interrupt
ldr pc, _prefetch_abort
ldr pc, _data_abort
ldr pc,
_not_used
ldr pc, _irq
ldr pc, _fiq
/* exception vector의 위치 정의 word(4byte)로 정의한것.
*/
_undefined_instruction: .word undefined_instruction
_software_interrupt: .word
software_interrupt
_prefetch_abort: .word prefetch_abort
_data_abort: .word
data_abort
_not_used: .word not_used
_irq: .word irq
_fiq: .word
fiq
.balignl 16,0xdeadbeef
/*
*************************************************************************
*
*
Startup Code (reset vector)
*
* do important init only if we
don't start from memory!
* relocate armboot to ram
* setup stack
*
jump to second stage
*
*************************************************************************
*/
_TEXT_BASE:
.word TEXT_BASE
.globl _armboot_start
_armboot_start:
.word _start
/*
* These are defined in the board-specific linker script.
*/
.globl
_bss_start
_bss_start:
.word __bss_start
.globl _bss_end
_bss_end:
.word _end
#ifdef CONFIG_USE_IRQ
/* IRQ stack memory (calculated at run-time)
*/
.globl IRQ_STACK_START
IRQ_STACK_START:
.word 0x0badc0de
/* IRQ stack memory (calculated at run-time) */
.globl
FIQ_STACK_START
FIQ_STACK_START:
.word 0x0badc0de
#endif
/*
* the actual reset code
*/
/*******************************************************
* 5가지 동작을 한다.
* 1) CPU를 Supervisor mode로 set
2)interrupt를 disable
* 3)watchdog을 turn off 4)clock을 setting
5)memory를 setting
*/
reset:
/*
* set the cpu to SVC32 mode
*/
mrs r0,cpsr
bic r0,r0,#0x1f // mode bit(하위 5bit)를 클리어 한다.
orr r0,r0,#0xd3 // interrupt를 disable, supervisor mode로 한다.
msr cpsr,r0
/* turn off the
watchdog */
#if defined(CONFIG_S3C2400)
# define
pWTCON 0x15300000
# define INTMSK 0x14400008 /* Interupt-Controller
base addresses */
# define CLKDIVN 0x14800014 /* clock divisor
register */
#elif defined(CONFIG_S3C2410) || defined(CONFIG_S3C2440)
/* 만약에 S3C2440이면 아래 정의된 주소로 레지스터가 잡힌다. 자세한
레지스터용도및 주소는 S3C2440의 데이터시트를 참조하세요*/
# define
pWTCON 0x53000000
# define INTMSK 0x4A000008 /* Interupt-Controller
base addresses */
# define INTSUBMSK 0x4A00001C
# define
CLKDIVN 0x4C000014 /* clock divisor register */
#endif
/* 2440이나 2410이면 아래와 같이 watchdog을 turn off하고
클럭을 셋팅한다는 내용이다. 필자의 대상보드는 2440이므로 분석 pass*/
#if
defined(CONFIG_S3C2400) || defined(CONFIG_S3C2410)
ldr r0,
=pWTCON
mov r1, #0x0
str r1, [r0]
/*
* mask all IRQs by setting all bits in
the INTMR - default
*/
mov r1, #0xffffffff
ldr r0,
=INTMSK
str r1, [r0]
# if
defined(CONFIG_S3C2410) /* 2410일 경우 interrupt submask register를
masking한다. */
ldr r1, =0x3ff /* 11bit이므로 */
ldr r0, =INTSUBMSK
str r1,
[r0]
# endif
/* FCLK:HCLK:PCLK = 1:2:4 */
/* default FCLK is 120 MHz ! */
ldr r0,
=CLKDIVN
mov r1, #3
str r1, [r0]
#endif /* CONFIG_S3C2400 ||
CONFIG_S3C2410 */
/* 만약 2440이면 아래와 같이 watchdog을 turn off하고
클럭을 셋팅한다. 필자가 사용하는 보드가 나왔다. 분석 들어간다.역시 자세한 사항은 S3C2440의 데이터시트를 참조하길
바란다.*/
#if defined(CONFIG_S3C2440)
ldr r0, =pWTCON /* r0로 pWTCON이 들어있는 번지 로딩 */
mov r1,
#0x0 /* r1에 0을 넣고 */
str r1,
[r0] /* r1의 값을 r0가 가리키는 곳의 내용으로 넣는다. */
/* mask all IRQs by setting all bits in the
INTMR - default *//* 부팅시 방해될 수 있는 인터럽트를 마스크한다. */
mov r1,
#0xffffffff
ldr r0, =INTMSK /* INTMSK가 있는 번지
로딩 */
str r1, [r0] /* INTMSK가 있는 번지에
0xffffffff을 넣는다. */
ldr r1, =0x7fff /*
r1에 0x7fff이 있는 번지 로딩 */
ldr r0, =INTSUBMSK /* r0에 INTSUBMSK가 있는 번지 로딩 */
str r1,
[r0] /* INTSUBMSK가 있는 번지에 0x7fff를 넣는다. */
/* FCLK:HCLK:PCLK = 1:3:6 */ @ clock setting
/*
default FCLK is 379.2 MHz ! */
ldr r0, =CLKDIVN @ CLKDIVN의 주소 0x4C000014
mov r1, #7 /* #7 = 0b0111, HDIVN = 3,
PDIVN = 1
str r1, [r0] /* FCLK :
HCLK : PCLK = 379.2 : 379.2/3 : 379.2/6
/* ghcstop add, ==> Clock asynchronous mode */
mrc
p15, 0, r1, c1, c0, 0 /* read ctrl
register */
orr r1, r1, #0xc0000000
mcr p15, 0, r1, c1, c0, 0 /* write ctrl register */
#endif /* CONFIG_S3C2440 */
/*
* we do sys-critical inits only at reboot,
* not when
booting from ram!
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_INIT_CRITICAL
bl cpu_init_crit /*
cpu_init_crit 서브루틴을 호출한다. cpu_init_crit는 좀 더 아래에 선언되어 있다.*/
#endif
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
/* memsetup.s 에서 복귀하여 armboot를 ram으로 재배치한다. */
relocate: /*
relocate U-Boot to RAM */
adr r0, _start /* r0 <-
current position of code */
ldr r1, _TEXT_BASE /* test
if we run from flash or RAM */
cmp r0,
r1 /* don't reloc during debug */
beq
stack_setup
ldr r2, _armboot_start
ldr r3, _bss_start
sub r2, r3, r2 /*
r2 <- size of armboot */
add r2, r0, r2 /* r2 <-
source end address */
copy_loop:
ldmia r0!, {r3-r10} /* copy from source address
[r0] */
stmia r1!, {r3-r10} /* copy to target address [r1]
*/
cmp r0, r2 /* until source end addreee [r2] */
ble copy_loop
/* Set up the stack */
stack_setup: /* stackpoint를 설정. */
ldr r0, _TEXT_BASE /*
upper 128 KiB: relocated uboot */
sub r0, r0, #CFG_MALLOC_LEN /*
malloc area */
sub r0, r0, #CFG_GBL_DATA_SIZE
/* bdinfo */
#ifdef CONFIG_USE_IRQ
sub r0,
r0, #(CONFIG_STACKSIZE_IRQ+CONFIG_STACKSIZE_FIQ)
#endif
sub sp,
r0, #12 /* leave 3 words for abort-stack */
clear_bss:
ldr r0, _bss_start /* find start of bss
segment */
ldr r1, _bss_end /* stop
here */
mov r2, #0x00000000 /*
clear */
clbss_l:str r2, [r0] /* clear loop... */
add r0,
r0, #4
cmp r0, r1
bne clbss_l
#if 0
/* try doing this stuff after the relocation */
ldr
r0, =pWTCON
mov r1, #0x0
str r1, [r0]
/*
* mask all IRQs by setting all bits in the INTMR - default
*/
mov r1, #0xffffffff
ldr r0, =INTMR
str r1, [r0]
/* FCLK:HCLK:PCLK = 1:2:4 */
/* default FCLK is 120 MHz ! */
ldr r0,
=CLKDIVN
mov r1, #3
str r1, [r0]
/* END stuff after
relocation */
#endif
ldr pc, _start_armboot /* Board.c에 포함되어 있는
_start_armboot함수로 branch한다. 실제 위치는 아래 선언된 start_armboot의 위치이다. 여기서
start.s의 동작은 완료되고 이제 RAM에서 남은 부팅절차가 수행된다. */
_start_armboot: .word
start_armboot
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
/* @
************************************************************************* @
* @
*
CPU_init_critical registers
*
* setup important registers
*
setup memory timing
*
*************************************************************************
*/
/* 이 루틴에서 p15는 CP15(coprocessor)를 말하고, c0~c15는 해당 coprocessor의
register를 말하는 것이다. */
/* mcr은 register to coprocessor, mrc는
coprocessor to register */
cpu_init_crit:
/*
* flush v4 I/D caches
*/
mov r0, #0 /* flush : 기억장치 내부의 내용을 지우는 것. 자세한 사항은 S3C2440의 데이터시트를
참조하길 바란다.*/
mcr p15, 0, r0, c7, c7, 0 /* flush v3/v4 cache */
mcr p15,
0, r0, c8, c7, 0 /* flush v4 TLB */
/*
* disable MMU stuff and caches
*/
mrc p15, 0, r0,
c1, c0, 0
bic r0, r0, #0x00002300 @ clear bits 13, 9:8 (--V- --RS)
bic r0,
r0, #0x00000087 @ clear bits 7, 2:0 (B--- -CAM)
orr r0, r0,
#0x00000002 @ set bit 2 (A) Align
orr r0, r0, #0x00001000 @ set bit
12 (I) I-Cache
mcr p15, 0, r0, c1, c0, 0
/*
* before relocating, we have to setup RAM timing
*
because memory timing is board-dependend, you will
* find a
memsetup.S in your board directory.
*/
mov ip, lr /* 다시 bl을 이용하므로 lr을 ip레지스터로 이동. */
bl memsetup /* memsetup을 호출
-> go to the memsetup.s 여기에서 memsetup.s로 제어가 넘어간다. memsetup.s는
/board/aesop2440/에 위치해있다. memsetup은 다음 포스트에 올리겠다. 넘어가보자. */
mov lr,
ip /* 서브루틴을 요청햇던 곳으로 이동하기 위해서 ip값을 lr레지스터로
이동. */
mov pc, lr /* 서브루틴을 호출한 곳으로 복귀. 위쪽 reset의 마지막 부분이었다. */
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
/*
*************************************************************************
*
*
Interrupt handling
*
*************************************************************************
*/
@
@ IRQ stack frame.
@
#define S_FRAME_SIZE 72
#define S_OLD_R0 68
#define S_PSR 64
#define S_PC 60
#define
S_LR 56
#define S_SP 52
#define S_IP 48
#define S_FP 44
#define S_R10 40
#define
S_R9 36
#define S_R8 32
#define S_R7 28
#define S_R6 24
#define
S_R5 20
#define S_R4 16
#define S_R3 12
#define S_R2 8
#define
S_R1 4
#define S_R0 0
#define MODE_SVC 0x13
#define I_BIT 0x80
/*
* use bad_save_user_regs for abort/prefetch/undef/swi ...
*
use irq_save_user_regs / irq_restore_user_regs for IRQ/FIQ handling
*/
.macro bad_save_user_regs
sub sp, sp, #S_FRAME_SIZE
stmia sp,
{r0 - r12} @ Calling r0-r12
ldr r2, _armboot_start
sub r2,
r2, #(CONFIG_STACKSIZE+CFG_MALLOC_LEN)
sub r2, r2,
#(CFG_GBL_DATA_SIZE+8) @ set base 2 words into abort stack
ldmia r2,
{r2 - r3} @ get pc, cpsr
add r0, sp, #S_FRAME_SIZE @ restore
sp_SVC
add r5, sp, #S_SP
mov r1, lr
stmia r5, {r0 - r3} @ save
sp_SVC, lr_SVC, pc, cpsr
mov r0, sp
.endm
.macro irq_save_user_regs
sub sp, sp, #S_FRAME_SIZE
stmia sp,
{r0 - r12} @ Calling r0-r12
add r8, sp, #S_PC
stmdb r8,
{sp, lr}^ @ Calling SP, LR
str lr, [r8,
#0] @ Save calling PC
mrs r6, spsr
str
r6, [r8, #4] @ Save CPSR
str r0, [r8,
#8] @ Save OLD_R0
mov r0, sp
.endm
.macro irq_restore_user_regs
ldmia sp, {r0 - lr}^ @ Calling r0
- lr
mov r0, r0
ldr lr, [sp, #S_PC] @ Get PC
add sp, sp,
#S_FRAME_SIZE
subs pc, lr, #4 @ return & move spsr_svc into
cpsr
.endm
.macro get_bad_stack
ldr r13, _armboot_start @ setup our mode
stack
sub r13, r13, #(CONFIG_STACKSIZE+CFG_MALLOC_LEN)
sub r13,
r13, #(CFG_GBL_DATA_SIZE+8) @ reserved a couple spots in abort stack
str lr, [r13] @ save caller lr / spsr
mrs lr, spsr
str
lr, [r13, #4]
mov r13, #MODE_SVC @ prepare SVC-Mode
@ msr spsr_c, r13
msr spsr,
r13
mov lr, pc
movs pc, lr
.endm
.macro get_irq_stack @ setup IRQ stack
ldr sp, IRQ_STACK_START
.endm
.macro get_fiq_stack @ setup FIQ stack
ldr sp, FIQ_STACK_START
.endm
/*
* exception handlers
*/
.align 5
undefined_instruction:
get_bad_stack
bad_save_user_regs
bl
do_undefined_instruction
.align 5
software_interrupt:
get_bad_stack
bad_save_user_regs
bl
do_software_interrupt
.align 5
prefetch_abort:
get_bad_stack
bad_save_user_regs
bl
do_prefetch_abort
.align 5
data_abort:
get_bad_stack
bad_save_user_regs
bl
do_data_abort
.align 5
not_used:
get_bad_stack
bad_save_user_regs
bl
do_not_used
#ifdef CONFIG_USE_IRQ
.align 5
irq:
get_irq_stack
irq_save_user_regs
bl
do_irq
irq_restore_user_regs
.align 5
fiq:
get_fiq_stack
/* someone ought to write a
more effiction fiq_save_user_regs */
irq_save_user_regs
bl
do_fiq
irq_restore_user_regs
#else
.align 5
irq:
get_bad_stack
bad_save_user_regs
bl
do_irq
.align 5
fiq:
get_bad_stack
bad_save_user_regs
bl
do_fiq
#endif
.align 5
.globl reset_cpu
reset_cpu:
#ifdef CONFIG_S3C2400
bl disable_interrupts
#
ifdef CONFIG_TRAB
bl disable_vfd
# endif
ldr r1, _rWTCON
ldr r2,
_rWTCNT
/* Disable watchdog */
mov r3, #0x0000
str r3, [r1]
/*
Initialize watchdog timer count register */
mov r3, #0x0001
str r3,
[r2]
/* Enable watchdog timer; assert reset at timer timeout */
mov r3,
#0x0021
str r3, [r1]
_loop_forever:
b _loop_forever
_rWTCON:
.word 0x15300000
_rWTCNT:
.word 0x15300008
#else
/* ! CONFIG_S3C2400 */
mov ip, #0
mcr p15, 0, ip, c7,
c7, 0 @ invalidate cache
mcr p15, 0, ip, c8, c7,
0 @ flush TLB (v4)
mrc p15, 0, ip, c1, c0, 0
@ get ctrl register
bic ip, ip, #0x000f @
............wcam
bic ip, ip, #0x2100 @
..v....s........
mcr p15, 0, ip, c1, c0, 0 @ ctrl
register
mov pc, r0
#endif /* CONFIG_S3C2400 */
---------------
출처 : http://blog.naver.com/idrukawa/100054113199
 u-boot-1.1.6.tar.bz2
u-boot-1.1.6.tar.bz2